¿POR QUÉ ES IMPORTANTE ESTUDIAR HISTORIA?
"EL CONOCIMIENTO NOS HARÁ LIBRES" Sócrates.8
ETAPAS DE LA HISTORIA
"EL CONOCIMIENTO NOS HARÁ LIBRES" Sócrates.8
ETAPAS DE LA HISTORIA
Gracias a la información de los extraordinarios blogs de los profesores Juanjo Romero, Julia García y Garófano Sociales de los cuales he extraído gran parte de los recursos incluidos aquí.
PUEBLOS GERMÁNICOS
Invasión de los pueblos germánicos sobre el Imperio Romano
EL ISLAM Y SU EXPANSIÓN
Presentación sobre el Islam y el arte islámico
THE SPREAD OF ISLAMIC EMPIRE
Web about the islamic spread



http://esquemasdehistoria.blogspot.com.es

IMPERIO CAROLINGIO
LOS FRANCOS
EL ISLAM Y SU EXPANSIÓN
Presentación sobre el Islam y el arte islámico
Web about the islamic spread



http://esquemasdehistoria.blogspot.com.es

AL ANDALUS
CIUDAD ANDALUSÍ
Medieval History of Spain
Medieval Spain was a battlefield where Christians attempted to regain control from the Moors, who had invaded the country before the 8th century. The Moors were intent of conquering all of Western Europe, but they were stopped in the Pyrenees by Charles the Hammer. This defeat left the invaders settling in the lower parts of the country. The early years of Moorish influence in medieval Spain were marked by infighting amongst the Muslim kingdoms. The Basques, who were traditionally fiercely independent, sided with French forces to expel the Moors.
The Moors' influence on Spain during the Middle Ages is still very evident. More than 4,000 words of Arabic origin are used in modern Spanish. Moorish architecture can be found throughout Spain, with its slender columns, horseshoe arches, cupolas, and airy, colorful buildings. Geometric designs and patterns can be found in surviving religious buildings, as the Koran forbade depicting human figures in places of worship.
Medieval Jews in Spain who had found themselves to be victims of northern invaders were held in high esteem by many of the Moorish leaders. They were valued as merchants and ambassadors and were often taken into the leaders' confidence. However, as the crusaders returned home, much of the hatred felt by these knights and soldiers was taken out on Jewish populations. The plague of 1391 led many to believe it was the work of Jews, and this led to a wave of anti-Semitism and the burning of Jewish villages and ghettoes.
The reconquest of Spain lasted nearly 800 years, and the story of these holys wars can be found in such medieval literary masterpieces such as El Cantar del Mio Cid (El Cid) and France's La Chanson de Roland (The Song of Roland).
A dark era in Spain's medieval history took place with the establishment of the Spanish Inquisition in 1480. Inquisitors tortured and killed those they suspected of being heretics and false converts from the Jewish and Muslim faiths. The guilty faced imprisonment, hanging, beheading, and burning at the stake.
UNIDAD 3: LA EUROPA MEDIEVAL
EUROPA EN EL AÑO 1000
ORÍGENES DEL FEUDALISMO
LA SOCIEDAD FEUDAL
LA SOCIEDAD FEUDAL
SERVIDUMBRE: El noble controlaba el territorio concedido por el rey (feudo) y a su población. Dada la inestabilidad política y militar de la época, los campesinos se sometieron a la autoridad del noble a cambio de su protección. Dejaron de ser completamente libres y se conviertieron con en siervos.
RELACIONES DE VASALLAJE
VASALLAJE: Era el sistema por el cual los nobles juraban fidelidad al rey y le prometían ayuda militar y consejo político. A cambio el rey le concedía al noble el control político, económico y militar de un territorio (feudo). La ceremonia en la que el noble juraba fidelidad al rey se denominaba homenaje y la investidura, por la que el rey cedía una porción de tierras, el feudo, a su vasallo.
Los nobles más importantes podían repetir sobre nobles segundones el sistema de vasallaje jurando fidelidad a cambio de territorios.
EL PODER DEL SEÑOR FEUDAL
FEUDO
PIRÁMIDE SOCIAL
NOBLEZA
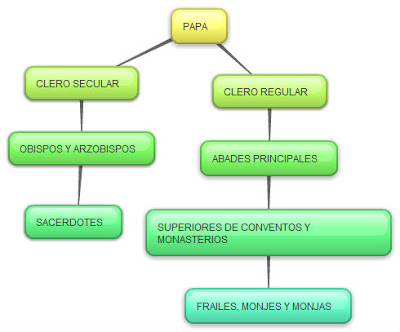
CLERO
MONASTERIO
CICLO AGRÍCOLA
Free powerpoints about the Middle Ages
Feudalism
SOCIAL STRUCTURE
UNIDAD 4
FORMACIÓN Y EXPANSIÓN DE LOS REINOS CRISTIANOS EN LA PENÍNSULA IBÉRICA
EXPANSIÓN DE LOS REINOS PIRENAICOS SIGLOS IX-XI
EVOLUCIÓN DE LOS REINOS CRISTIANOS
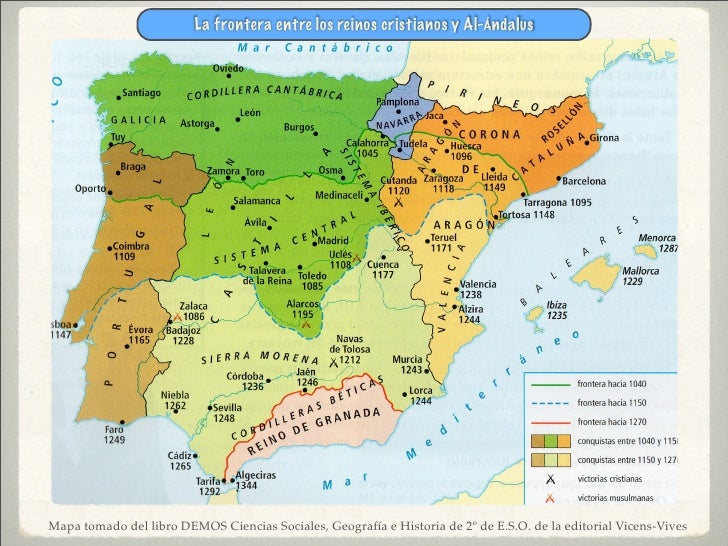
EXPANSIÓN DE LOS REINOS CRISTIANOS DURANTE LOS SIGLOS XI, XII Y XIII

REINOS DURANTE EL SIGLO XV
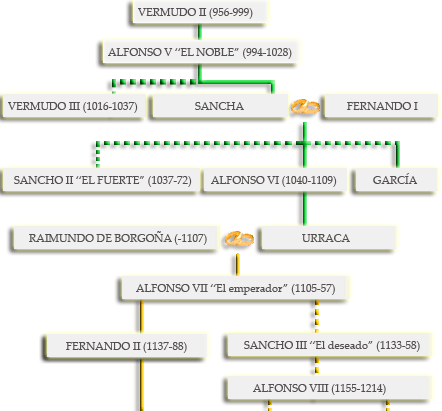
ÁRBOL GENEALÓGICO DE LA MONARQUÍA ESPAÑOLA
ARTE ANDALUSÍ
ARTE ROMÁNICO
PLANTA DE UNA IGLESIA ROMÁNICA

Escultura y pintura del Románico
EL ARTE DE LAS CIUDADES: EL GÓTICO
PLANTA DE UNA CATEDRAL GÓTICA
IMÁGENES DE ARTE ROMÁNICO Y GÓTICO ESPAÑOLAS
ROMÁNICO
EL CAMINO DE SANTIAGO
GÓTICO
LA CIUDAD MEDIEVAL

IMAGEN DE UNA CIUDAD MEDIEVAL

CIUDAD DE ÁVILA

PLANO DE MADRID MEDIEVAL
LA CIUDAD MEDIEVAL
ROTACIÓN TRIENAL
LA PESTE NEGRA
THE PRINTING PRESS
LOS VIAJES DE MARCO POLO
RUTAS COMERCIALES DURANTE LOS SIGLOS XIV Y XV
RENACIMIENTO

EDAD MODERNA EN ESPAÑA
LOS REYES CATÓLICOS: ISABEL Y FERNANDO
POSESIONES DE LOS REYES CATÓLICOS
ALIANZAS MATRIMONIALES
LOS GRANDES DESCUBRIMIENTOS GEOGRÁFICOS
EL DESCUBRIMIENTO DE AMÉRICA
LOS VIAJES DE CRISTOBAL COLÓN
LOS IMPERIOS PRECOLOMBINOS Y LOS CONQUISTADORES
LOS DESCUBRIMIENTOS GEOGRÁFICOS
CARLOS I
HERENCIA DE CARLOS I DE ESPAÑA
FELIPE II

EUROPA Y ESPAÑA DEL SIGLO XVII
GEOGRAPHY
DEMOGRAPHY

PIRÁMIDES DE POBLACIÓN
DEMOGRAFÍA EN ESPAÑA
ENVEJECIMIENTO EN ESPAÑA
Mapa político mudo de España